
VPN – short for ‘Virtual Private Network’, enables its user to connect to the internet via a secure and encrypted connection.
The connection is encrypted in real time as soon as a connection with a VPN is established. This is a great way to stop your ISP or other third parties from tracking and stealing your data online.
- What is a VPN Tunnel?
- Why would you need a VPN?
- Who uses a VPN?
- How does a VPN work?
- How much does a VPN cost?
- What’s the difference between free & paid VPNs?
- How to set up and use a VPN?
- Is a Proxy the same thing as a VPN?
- What are the different types of VPNs? What kind of VPNs are there?
- How to choose the best VPN for yourself?
- What are the different protocols in a VPN?
- What devices can I protect with a VPN?
- What is the difference between a physical VPN server and a cloud VPN server?
What is a VPN Tunnel?
A VPN tunnel is a secure and encrypted connection between two devices that are connected to the internet. When you use a VPN, your internet traffic is routed through a VPN server, which creates a VPN tunnel between your device and the VPN server. This VPN tunnel encrypts your data, making it difficult for third parties to access or intercept your data.
Think of a VPN tunnel as a virtual, encrypted tunnel that is created between your device and the VPN server. Your data is sent through this tunnel, where it is encrypted and protected from being accessed by third parties. Once the data reaches the VPN server, it is decrypted and sent to its destination on the internet.
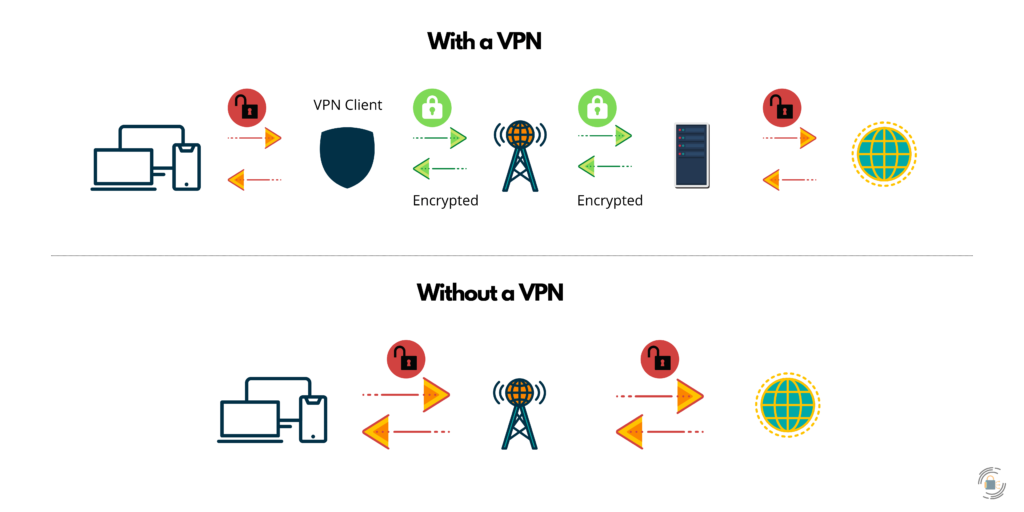
In this way, a VPN tunnel provides an additional layer of security and privacy to your internet connection, allowing you to browse the internet securely and anonymously. VPN tunnels are commonly used by individuals and organizations to protect their data and privacy online.
Why would you need a VPN?
There are several reasons why you might need a VPN, some of them being:
To protect your privacy online
It can help to protect your privacy by encrypting your internet connection and hiding your IP address. This can prevent third parties, such as advertisers or government agencies, from tracking your online activity.
To access content that is restricted in your location
Some content, such as streaming services or websites, may be restricted based on your location. A VPN can help you to access this content by routing your internet connection through a server in a different location.
To securely connect to a public Wi-Fi network
Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, which makes it easy for third parties to access your data. A VPN can help to protect your data when using a public Wi-Fi network by encrypting your internet connection.
To securely connect to a corporate network
If you work remotely, a VPN can help you to securely connect to your company’s network, allowing you to access corporate resources and data.
Overall, a VPN can provide an additional layer of security and privacy to your internet connection, and can help you to access content that might be restricted in your location.
Who uses a VPN?
A virtual private network (VPN) is used by individuals and organizations to provide an additional layer of security and privacy to their internet connection. People might use a VPN for a variety of reasons, such as to protect their privacy online, to access content that is restricted in their country, or to securely connect to a corporate network.
How does a VPN work?
A VPN works by routing your device’s internet connection through a secure server that encrypts the data that is sent and received. This encrypted data is then sent to a VPN server, which is typically located in a different country, where it is decrypted and sent to its original destination. This process allows the user to browse the internet anonymously and securely, as well as access content that might be restricted in their location.
Here’s a simple example of how a VPN works:
- You connect to the internet using a VPN client on your devices, such as a laptop or smartphone.
- The VPN client encrypts the data that is sent and received by your device.
- The encrypted data is sent to a VPN server, which is located in a different location than you.
- The VPN server decrypts the data and sends it to its original destination on the internet.
- The data is then received by the destination server and delivered back to you.
How much does a VPN cost?
Paid VPNs typically start at around $10 per month for a basic plan, and can go up to $20 to $30 per month for more advanced plans with additional features.
The cost of a VPN can vary depending on the provider and the specific plan you choose. Yearly or multi-year plans are generally cheaper and you can get a good deal on them where the cost of a month may come down to the range of $1 – $3 depending on the provider.
Some providers may offer discounts or promotions, so it’s worth shopping around to find the best deals, especially during the holiday season.
What’s the difference between free & paid VPNs?
Free and paid VPNs both provide an additional layer of security and privacy to your internet connection, but there are some key differences between the two. One of the main differences is the level of security and privacy provided.
Free VPNs
Often have fewer servers and server locations to choose from, which can limit your ability to access certain content. They may also have slower connection speeds and fewer features, such as the ability to switch between server locations. In addition, free VPNs may collect and sell your data to third parties, or display ads to generate revenue.
Paid VPNs
Typically offer a wider range of server locations, faster connection speeds, and more advanced features. They also provide a higher level of security and privacy, as they do not collect or sell your data to third parties, and do not display ads. In addition, paid VPNs often have dedicated customer support teams that can help you with any issues or questions you might have.
Another difference between free and paid VPNs is the level of trust and reputation. Free VPNs may not have the same level of trust and reputation as paid VPNs, as they may be more likely to collect and sell your data, or to display ads. Paid VPNs, on the other hand, have generally built up a reputation for providing a high level of security and privacy to their users.
In general, paid VPNs provide a higher level of security, privacy, and trust than free VPNs, but they may come at a cost. It’s important to carefully consider your needs and budget when deciding whether to use a free or paid VPN.
How to set up and use a VPN?
To set up and use a VPN, you will need to follow these steps:
- Choose a VPN provider. There are many different VPN providers available, so it’s important to research and compare your options to find one that meets your needs and budget.
- Sign up for a VPN account with the provider you have chosen. This will typically involve providing your email address and payment information.
- Download and install the VPN client on your device. Most VPN providers will have a client app that you can download and install on your devices, such as a laptop or smartphone.
- Launch the VPN client and log in to your VPN account.
- Choose a server location and connect to the VPN. Most VPN clients will allow you to choose from a list of server locations, so you can select one that is appropriate for your needs. Once you have chosen a server location, click on the “Connect” button to establish a VPN connection.
- Use the internet as you normally would. Once you are connected to the VPN, you can browse the internet as you normally would, but your traffic will be routed through the VPN server and encrypted, providing an additional layer of security and privacy.
To disconnect from the VPN, simply click on the “Disconnect” button in the VPN client.
Is a Proxy the same thing as a VPN?
A proxy and a VPN are both types of networking technologies that can be used to provide an additional layer of security and privacy to your internet connection. However, there are some key differences between the two.
Proxy
It is a server that acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. When you connect to the internet through a proxy, your traffic is routed through the proxy server, which can help to mask your IP address and protect your privacy online. However, a proxy does not encrypt your internet connection, so your data is not secure when using a proxy.
VPN
On the other hand, a VPN is a more secure type of technology that encrypts your internet connection. When you connect to the internet through a VPN, your traffic is routed through a secure VPN server, which encrypts your data and hides your IP address. This provides a higher level of security and privacy than a proxy, as your data is encrypted and cannot be easily accessed by third parties.
In general, a VPN provides a higher level of security and privacy than a proxy, but a proxy may be sufficient for some users who only need a basic level of protection. It’s important to carefully consider your needs and budget when deciding whether to use a proxy or a VPN.
What are the different types of VPNs? What kind of VPNs are there?
There are several different types of VPNs, each with its own set of features and capabilities. Some of the main types of VPNs include:
Remote-access VPNs
These are the most common type of VPNs and are used by individuals and organizations to securely connect to a remote network, such as a corporate network. Remote-access VPNs typically use software that is installed on the user’s device and require authentication to access the VPN.
Site-to-site VPNs
These VPNs are used to connect multiple networks, such as connecting an office network to a remote branch office. Site-to-site VPNs typically use hardware devices, such as routers, to establish and maintain the VPN connection.
Mobile VPNs
Mobile VPNs are designed specifically for use on mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. Mobile VPNs use software that is installed on the user’s device and can automatically establish a VPN connection when the device connects to the internet.
Virtual private LAN (VPLS)
This type of VPN uses a virtual private local area network (LAN) to connect multiple sites. VPLS is often used in situations where the sites are located in different locations but need to share resources and data.
Each type of VPN has its benefits and drawbacks, and the right type for you will depend on your specific needs and requirements.
How to choose the best VPN for yourself?
When choosing a VPN, it’s important to consider a few key factors to find the best option for your needs. Some things to consider when choosing a VPN include:
- Security: The security of a VPN is one of the most important factors to consider. Look for one that uses strong encryption and offers a range of security features, such as a kill switch and DNS leak protection.
- Privacy: Always check to see if the provider has a strict no-logs policy, so that your data is not collected or shared with third parties.
- Speed: The speed of a VPN can vary depending on the server location and the number of users connected to the server. Look for a one that offers fast connection speeds and allows you to switch between server locations.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the VPN is compatible with your devices and operating systems. Most VPNs have client apps that can be downloaded and installed on a range of devices, but some may only be available for certain platforms.
- Price: VPNs can vary in price, so it’s important to consider your budget when choosing a provider. Keep in mind that free VPNs may not offer the same level of security and privacy as paid VPNs.
By considering these factors, you can find the best VPN for your needs. It’s also a good idea to read reviews and compare different VPNs before making a decision.
What are the different protocols in a VPN?
VPN protocols are the set of rules that are used to establish and maintain a secure VPN connection. There are several different VPN protocols available, each with its own set of features and security capabilities. Some of the most commonly used VPN protocols include:
OpenVPN
This is an open-source VPN protocol that is widely considered to be the most secure and versatile option. It uses a combination of SSL/TLS and the OpenSSL encryption library to provide a high level of security and privacy.
L2TP/IPSec
This is a secure VPN protocol that is often used in combination with the Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) protocol. It provides strong encryption and authentication but can be slower and more resource-intensive than other VPN protocols.
PPTP
This is an older VPN protocol that is not as secure as other options but is faster and easier to set up. It is not recommended for use in situations where security is a high priority.
SSTP
This is a secure VPN protocol that is often used in corporate environments. It uses the Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) to encrypt traffic and is typically only available on Windows devices.
When choosing a VPN protocol, it’s important to consider factors such as security, speed, and compatibility with your devices. The right protocol for you will depend on your specific needs and preferences.
What devices can I protect with a VPN?
Most VPN providers offer client apps that can be downloaded and installed on a wide range of devices, including:
Desktop computers & laptops
VPNs can be installed on desktop computers running Windows, macOS, or Linux operating systems.
Smartphones & tablets
They can also be installed on smartphones running Android, iOS, or other mobile operating systems.
Routers
Some VPN providers even offer VPN-compatible routers that can be used to protect all of the devices on your home network.
What is the difference between a physical VPN server and a cloud VPN server?
The main difference between a physical VPN server and a cloud VPN server is where the server is located and how it is accessed.
A physical VPN server is a server that is located in a physical location, such as a data center or office building. It is typically owned and managed by the VPN provider, and users connect to the server using a VPN client installed on their device.
A cloud VPN server, on the other hand, is a virtual server that is hosted on a cloud computing platform, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure. Cloud VPN servers are accessed over the internet, and users can connect to them using a VPN client or a web browser.
There are several key differences between physical and cloud VPN servers:
Location: A physical VPN server is located in a specific location, while a cloud VPN server is hosted on a cloud computing platform and can be accessed from anywhere.
Ownership: A physical VPN server is owned and managed by the VPN provider, while a cloud VPN server is typically owned and managed by the cloud computing provider.
Access: Physical VPN servers are typically accessed using a VPN client, while cloud VPN servers can be accessed using a VPN client or a web browser.
Overall, the main difference between a physical VPN server and a cloud VPN server is where the server is located and how it is accessed. Both types of servers can provide an additional layer of security and privacy to your internet connection, but the right option for you will depend on your specific needs and requirements.

